
Synopsis
Air-to-Air Missile- MICA, Astra
Surface to Surface Missile- Agni, Prithvi, Brahmos
Short Range SAM (Surface to Air)- Trishul (Precision issues led to the import of Barak Missiles from Israel.)
Medium Range SAM-Akash (3 variants)
Long Range SAM- Barak 8
Medium Range Ballistic Missile- Agni I
Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile- Agni II to Agni V
ICBM or Inter Continental Ballistic Missile- Agni V
Short Range Ballistic Missile- Prithvi I and II, Dhanush
Medium Range Ballistic Missile- Shaurya, Prahaar
Supersonic Cruise Missile- Brahmos I
Hypersonic Cruise Missile- Brahmos II
Subsonic Cruise Missile- Nirbhay
Submarine Launched Ballistic Missile- Sagarika K5
Anti-Tank Guided Missile- Nag, Amogha, Helina
The Indian Armed Forces uses various types of ballistic and cruise missiles. In India, the Defence Research and Development Organisation is the major body that is involved in the research and development of missiles. Public sector units (Bharat Dynamics Ltd-BDL, Bharat Electronics Ltd-BEL) and some of the private organizations (Tata Advanced Systems, Larsen & Toubro, and Kalyani Rafael Advanced Systems ) are involved in the manufacture of the missiles, often in collaboration with foreign manufacturers. India is one of seven countries in the world with intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and one of four countries with anti-ballistic missile systems. Since 2016, India has been a member of Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
Ballistic Missile Defence System
Aimed at intercepting aerial threat from ballistic missiles that have ranges up to 5000km at altitudes both outside (exo) and inside (endo) the atmosphere
1st layer: Endo
The single stage solid rocket-propelled Advanced Air Defence (AAD) low-altitude interceptor missile. (Ashwin) The AAD interceptor missile is primarily designed to intercept enemy missiles in the endo-atmosphere at altitudes of 20-40 kilometres.
2nd layer: Exo
Prithvi Air Defence Vehicle known as Pradyumna Ballistic Missile Interceptor is designed to destroy missiles with ranges 300-2000 km at exo-atmosphere (about 80km altitude).
First successful interception in 2006
For higher altitudes up to 150 km, Agni-V-based ballistic interceptors would be used. (because of 5000km range)
Multi-Layered Air Defence System: S-400
Alternatives: THAAD and Patriot
India has signed a deal with Russia to acquire S-400 TRIUMF multi-layered air defence system.
S-400 is known as Russia’s most advanced long-range surface-to-air missile defence system.
S-400 layered defence system can intercept all types of aerial targets including aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), and ballistic and cruise missiles up to the range of 400km, at an altitude of up to 30km
Capable of firing three types of missiles to create a layered defence.
USA is offering THAAD and Patriot as alternative to S-400 to India.
Barak-8 Long and Medium Range SAM (Surface to Air Missile)
Medium-range surface-to-air missile system being developed jointly by India and Isreal.
It will have an interception range of 70-100 km.
Part of naval air defence system to be used aboard INS Vikrant (under construction)
Maximum speed of Mach 2.
Notable Deployment: In Ladakh against China
Akash Medium-Range Surface to Air Missile System
India has 2 regiments of the indigenous Akash systems which are capable of multi-target engagement.
It can strike targets up to a range of 25km and altitude of 18,000m.
The Akash has been developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and manufactured by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL). It has become the backbone of India’s air defence system.
The Akash is a medium-range surface-to-air missile system designed to protect vital areas from aerial attacks. It can strike targets at distances of up to 45 kilometres and altitudes between 4 and 25 kilometres.
- Type: Medium-range surface-to-air missile (SAM)
- Range: Up to 45 km
- Altitude engagement: 4–25 km
- Targets: Fighter jets, cruise missiles, UAVs, air-to-surface missiles

Multi-layered Air Defence System for Delhi
India is developing a multi-layered air defence system for its cities besides air defence system for tactical battle areas.
1st layer: 2-tier Ballistic Missile Defence System
2nd Layer: S-400 layered defence system
3rd Layer: Barak-8 long and medium range SAM
4th Layer: Akash medium-range surface to air missile system
5th Layer: NASAMS-2
NASAMS-2
India is acquiring NASAMS-2 from US.
NASAMS 2 will form the inner-most layer of Delhi Area Air Defence Plan that has been conceived of.
It will be deployed to protect vital assets and people in the National Capital region of Delhi including President’s house, Parliament etc.
It renders quick-reaction 3-dimensional protection at low altitudes of 5 km to various types of aerial threats ranging from drones to ballistic missiles.
Hypersonic Missiles
Travels at Mach 5 or higher (more than one mile per second)
They typically consist of a Supersonic Combustion Ramjet or Scramjet propulsion system to enable such high speeds.
Scramjet engine collects oxygen from the atmosphere as it is travelling and mixes the oxygen with its hydrogen fuel, creating the combustion needed for hypersonic travel.
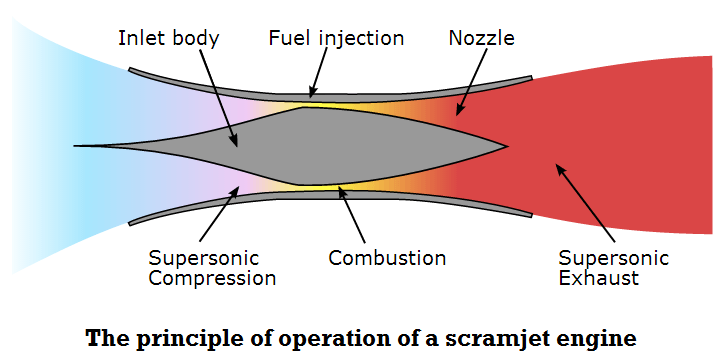
India is developing a Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV)
It is an unmanned scramjet (allowing supersonic combustion) demonstration vehicle that can cruise to a speed of Mach 6 (or six times the speed of sound) and rise up to an altitude of 32 km in 20 seconds. It has been developed by DRDO.
There are 2 types of Hypersonic Weapon Delivery Systems
Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCM)
Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV)
They are a mix of the speed of a ballistic missile and manoeuvring capabilities of a cruise missile
While cruise missiles achieve speeds of 550 mile per hour, the hypersonic missiles aircrafts can reach speeds more than 3500 miles per hour.
Capable of penetrating any antimissile defence system currently available that are designed to intercept cruise and ballistic missiles.
Specifically designed for increased survivability against modern ballistic missile defence systems.
Project Kusha is a major indigenous air defence initiative led by India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Its primary goal is to develop a long-range, multi-layered surface-to-air missile (SAM) system capable of countering advanced aerial threats, including hypersonic weapons traveling at speeds up to Mach 7 (about 8,645 km/h).
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board.
Panchi
- The wheeled variant of the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Nishant, can take off and land on tiny airstrips.
- It has all of the surveillance capabilities of the UAV Nishant plus greater endurance because it does not need to carry the airbags and parachute system that the UAV Nishant does.
Nishant UAV
- Inducted into the Army is a multi-mission UAV with Day/Night operational capability.
- Intended for battlefield surveillance, tracking and localization of targets, and artillery firing correction.
- Operated by an easy-to-use Ground Control Station + image processing system to examine UAV-sent images.
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT)
- India successfully tested its ASAT missile in March 2019.
- A live satellite in low Earth orbit was destroyed by the ASAT missile (283-kilometer).
- According to the DRDO, the missile can fire down objects traveling at a speed of 10 km per second from an altitude of 1200 km.
Pinaka Missile System
- Pinaka is an indigenous multi-barrel rocket launch system developed for the Indian Army by the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO).
- Its weapon system includes a cutting-edge guidance package, as well as an advanced navigation and control system.
- The Pinaka Mark-II Rocket is converted into a missile by integrating with the navigation, control, and guidance system, which improves accuracy and range.
- The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System assists the missile’s navigation system (IRNSS).
- It is an artillery missile system capable of striking enemy land with pinpoint accuracy up to a range of 75 kilometers.
- The weapon system’s first version, known as Mark I, had a range of 40 kilometers.
- The upgraded version of Pinaka Mark II has an extended range of 70 to 80 km.
Mission Shakti
Mission Shakti was launched to build highly effective anti-satellite weaponry (ASAT). It is a collaboration between the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) (ISRO).
ASAT (anti-satellite) system is a missile-based system used to attack moving satellites.
The primary objective of Mission Shakti was to demonstrate India’s capability to safeguard its space assets by developing the technology to shoot down satellites in orbit. The successful test showcased India’s anti-satellite missile technology.
- The successful test made India the fourth country in the world, after the United States, Russia, and China, to possess the capability to shoot down satellites in space.
- The test raised discussions and concerns about the militarization of space and the need for international norms and agreements regarding space activities.
Fact File
- India’s first indigenously developed missile was Prithvi, a short-range ballistic missile. It was developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP) and first tested in 1988. Prithvi is a surface-to-surface missile with a range of 150 km
- Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam spent four decades as a scientist and science administrator, mainly at the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and was intimately involved in India’s civilian space programme and military missile development efforts. He was known as the “Missile Man of India” for his work on the development of ballistic missile and launch vehicle technology. He also played a pivotal organisational, technical, and political role in Pokhran-II nuclear tests in 1998, India’s second such test after the first test in 1974.
- Operation Trident (India vs Pak 1971) saw the first use of anti-ship missiles in South east Asia region.
- Nag anti-tank missile is the only missile in the world to have full fibre glass body.
- The Brahmos are named after the rivers Brahmaputra and Moskva.
To get Saptarshi Sir’s guidance for PSC Miscellaneous Mains/ Clerkship Main/ English/Economy or for overall WBCS or other exam preparation, call or WhatsApp us @6295350330. Classes for PSC Miscellaneous Main and Clerkship Main have already started. WBCS New batch is also going on. You can also download our app for online guidance using the link
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=co.penny.oecgd&pcampaignid=web_share
For free notes, daily quizzes, word games and many other surprises, please join our Telegram Group using the link below









